An online textbook explaining photosynthesis and cellular respiration...
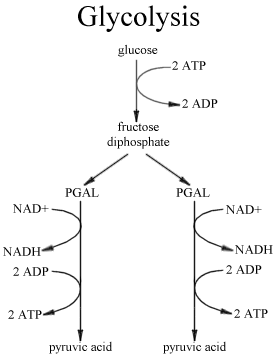
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a process that takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell. It is a process that breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvic acids. During this conversion, energy is lost in order to make ATP. Six carbons of glucose enter the process which then uses two ATP to split them into two 3 carbon pyruvic acid molecules. During this process, energy is lost. Four ADP come into the process in order to capture the lost energy to make 4 ATP molecules which are then utilized by the cell as energy. Next, two NAD+ molecules come in the same way ADP molecules to capture lost electrons to make two NADH. The reactants of glycolysis are glucose, ADP, ATP, and NAD+. The products are two pyruvic molecules, ADP, ATP, and NADH.