An online textbook explaining photosynthesis and cellular respiration...
Krebs Cycle
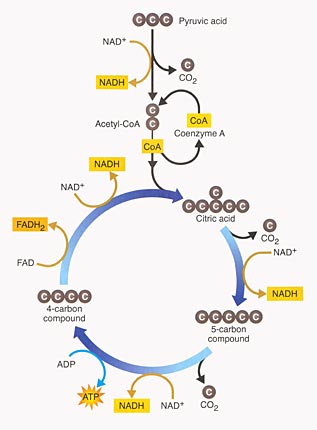
The Krebs cycle is a process that occurs in the mitochondrion of a cell. First, the pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle and will react with coenzyme A, otherwise known as CoA. This reaction results in the formation of a 2-carbon product named Acetyl – CoA. During this reaction, carbon dioxide is being released from the mitochondrion. Also, at this time, NAD+ molecules come into the reaction and “pick up” the electrons that are being lost. As they pick up these electrons, they become full and turn into NADH molecules. The Acetyl CoA then loses CoA, which then returns to the first step after combining with oxaloacetic acid, a product of the previous cycle. This reaction creates a six carbon molecule called citric acid. Next, citric acid releases CO2 and turns into a five carbon molecule called Ketoglutaric acid. During this process, NAD+ comes in and takes in lost electrons to turn into NADH. The newly formed Ketoglutaric acid loses another CO2 molecule. Another NAD+ comes in to take in lost electrons to become NADH. ADP also enters the cycle to take in lost energy to become ATP. After losing a carbon atom, the ketoglutaric acid becomes a four carbon molecule called Succinic acid. Unlike the previous steps, Succinic acid does not lose a carbon dioxide molecule. A FAD molecule (another electron carrier molecule) comes in to pick up electrons that are lost by Succinic acid to become full in order to turn into a molecule named FADH2. Malic acid is then formed (four carbons) and is approached by a NAD+ molecule that will pick up more electrons to turn into a NADH molecule. Malic acid is then turned back into oxaloacetic acid to continue the cycle. In two cycles and the process involved, for two pyruvic acids or one glucose molecule, the net products are six molecules of carbon dioxide, eight NADH molecules, two ATP molecules, and two FADH2 molecules. The reactants of both the Krebs cycle and the process involving CoA in two cycles include two pyruvic acid molecules, eight molecules of NAD+, two molecules of ADP, two FAD molecules, and CoA.